Fast food is quick and easy, but too much of it can harm your health. Look out for these signs that it might be time to cut back and make healthier choices.
Mood Swings


The high sugar and fat content in fast foods can lead to dramatic fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which can negatively impact mood.
Consuming fast food regularly has been linked to higher rates of anxiety and depression due to the lack of essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins, which support mental health.
Additionally, the brain’s reward system may become overstimulated by the hyper-palatable nature of fast foods, contributing to feelings of irritability or dependence.
These mood swings can worsen over time with excessive consumption, affecting your overall emotional well-being.
Elevated Blood Pressure
Fast foods are notoriously high in sodium, a primary contributor to high blood pressure. A single meal from a fast-food chain can contain more than the daily recommended amount of sodium, placing undue strain on the cardiovascular system.
Over time, this can increase the risk of developing hypertension and heart-related complications. Excess sodium also causes the body to retain water, which can further raise blood pressure levels.
For those already at risk, frequent consumption of fast food can significantly worsen the condition.

High Cholesterol Levels
Many fast food items are rich in trans fats and saturated fats, which are known to raise LDL (bad) cholesterol and lower HDL (good) cholesterol.
High cholesterol levels can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Even small amounts of trans fats, often found in fried foods, can have significant effects on cholesterol levels. Consuming fast food regularly can also make it challenging to balance cholesterol levels through diet alone.


Insulin Resistance
Sugary fast foods, like sodas and desserts, can spike blood sugar levels rapidly, forcing the pancreas to release large amounts of insulin.
Over time, this repeated strain on the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Insulin resistance occurs when cells no longer respond effectively to insulin, resulting in persistently high blood sugar levels.
Regularly consuming fast food increases this risk significantly, especially when combined with other factors like lack of exercise.


Digestive Issues
Fast foods are typically low in dietary fiber, an essential nutrient for maintaining healthy digestion. Without enough fiber, you may experience constipation, irregular bowel movements, and a slower digestive process.
Additionally, the high-fat content in many fast foods can delay stomach emptying, leading to feelings of discomfort or bloating.
Over time, a lack of fiber-rich foods can also harm gut health, affecting the balance of beneficial bacteria in the digestive system.


Fatigue
Fast food provides a quick burst of energy due to its high sugar and refined carbohydrate content, but this energy is short-lived. After the initial spike, blood sugar levels crash, leaving you feeling fatigued and sluggish.
The lack of essential nutrients like complex carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats in fast food also contributes to ongoing tiredness.
Chronic fatigue from poor diet choices can affect your productivity, mood, and overall quality of life.


Shortness of Breath
Frequent consumption of fast food can contribute to weight gain, which increases strain on the respiratory system. Carrying extra weight makes it harder for your lungs and diaphragm to expand fully, leading to shortness of breath during everyday activities.
This issue is more pronounced in individuals with preexisting conditions such as asthma or sleep apnea.
Over time, the added strain on the heart and lungs can lead to more serious respiratory complications.


Rapid Weight Gain
Fast food is calorie-dense but often lacks essential nutrients, making it easy to overeat without feeling satisfied. The high fat, sugar, and carbohydrate content contributes to rapid weight gain, particularly when consumed frequently.
Additionally, fast food is often served in oversized portions, further increasing calorie intake.
Weight gain from excessive fast food consumption is associated with numerous health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.


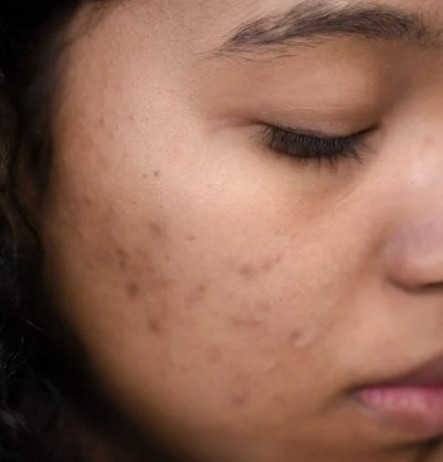
Skin Problems
Fast foods, especially those high in refined carbs and sugars, can increase insulin levels, triggering hormonal changes that lead to acne. Studies have shown that diets high in glycemic index foods can worsen skin conditions by promoting inflammation.
Greasy foods can also contribute to clogged pores if consumed excessively.
Reducing fast food intake and opting for a balanced diet with fresh fruits and vegetables can help improve skin health over time.


Dental Problems
The high sugar content in fast food items, including sodas and desserts, is a leading cause of cavities and tooth decay. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that erode tooth enamel and lead to dental problems.
Additionally, acidic beverages like sodas can weaken enamel further, increasing the risk of sensitivity and decay.
Over time, poor dental hygiene combined with a fast food-heavy diet can result in serious oral health issues.

Weakened Immune System
Fast foods often lack essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are critical for maintaining a strong immune system. Consuming excessive fast food can weaken your body’s ability to fight off infections and recover from illnesses.
Processed foods can also promote inflammation, which negatively impacts immune health over time.
A diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods is necessary to maintain a healthy and responsive immune system.


Increased Thirst
Fast foods are often loaded with sodium, which can disrupt your body’s fluid balance and cause dehydration. High sodium intake makes your body retain water, leaving you feeling bloated but paradoxically thirsty.
This increased thirst often leads people to consume sugary sodas or drinks, compounding the problem. Staying hydrated and limiting sodium consumption are key to avoiding these issues.


Bloating
Excessive salt and fat in fast foods can cause water retention and digestive discomfort, leading to bloating. Sodium encourages the body to hold onto water, making you feel puffier, especially in the abdomen and extremities.
Foods high in fats can also slow digestion, contributing to bloating and discomfort.
Reducing your intake of salty, processed foods can help alleviate these symptoms.


Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Greasy and fried fast foods are a common trigger for heartburn and acid reflux. These foods relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to rise into the esophagus.
The result is a burning sensation in the chest or throat, often made worse by large portions or eating late at night.
Chronic acid reflux can lead to more severe conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).


Joint Pain
Excessive weight gain from fast food consumption can strain joints, particularly in the knees, hips, and lower back. Obesity is a major risk factor for osteoarthritis, as the added pressure accelerates joint wear and tear.
Additionally, fast foods can promote inflammation in the body, which may worsen joint pain and stiffness. Maintaining a healthy weight and reducing inflammatory foods can improve joint health over time.


Sleep Disturbances
Eating fast food, especially late at night, can disrupt your sleep quality. High-fat and high-sugar meals can cause indigestion, making it harder to fall asleep or stay asleep.
Additionally, poor nutrition can lead to imbalances in hormones like melatonin and serotonin, which regulate sleep. Over time, lack of quality sleep can affect your energy, mood, and overall health.


Reduced Concentration and Focus
Fast foods often lack the nutrients needed to support optimal brain function, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. High-sugar and high-fat diets can impair memory and reduce your ability to concentrate.
Over time, a poor diet can even contribute to cognitive decline. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods into your diet can improve mental clarity and focus.


Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Fast food consumption is linked to fat deposits in the liver, leading to NAFLD. This condition occurs when excess fat accumulates in liver cells, impairing its function and increasing the risk of liver-related diseases.
High-fat and high-sugar diets are primary contributors to this condition, which often develops without noticeable symptoms in the early stages.
Reducing fast food intake and adopting a balanced diet can help prevent or manage NAFLD.


Increased Risk of Heart Disease
The combination of high sodium, trans fats, and cholesterol in fast foods significantly increases the risk of heart disease. These factors contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries, raising the likelihood of heart attack or stroke.
Over time, regular consumption of fast food can also lead to obesity, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular issues.
Prioritizing a heart-healthy diet is essential for reducing these risks.

Addiction-like Eating Behaviors
Fast foods are engineered to be hyper-palatable, combining high levels of sugar, fat, and salt to activate the brain’s reward centers. This can lead to overconsumption and addiction-like eating behaviors, making it difficult to control cravings.
The dopamine rush from these foods can reinforce a cycle of dependency, similar to substance abuse.
Breaking this cycle often requires mindful eating and replacing fast food with healthier alternatives.


Increased Inflammation
Fast foods promote chronic inflammation in the body due to their high content of unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives. Chronic inflammation is linked to a range of health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Inflammation can also exacerbate conditions like arthritis, leading to joint pain and stiffness. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, like leafy greens and berries, can help counteract these effects.


Slow Healing
A lack of vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and zinc, can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds. Fast foods often lack these nutrients, delaying recovery from injuries, illnesses, or surgeries.
Protein, which is vital for tissue repair, is also frequently insufficient in fast-food-heavy diets. Switching to a nutrient-dense diet can significantly improve your body’s ability to heal.


High Blood Sugar Levels
Fast foods that are high in refined carbohydrates and sugars can lead to sharp spikes in blood sugar levels. Over time, this repeated strain on blood sugar regulation can contribute to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Regularly consuming these foods increases the risk of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that includes high blood sugar. Replacing sugary snacks with whole foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels.


Loss of Appetite for Healthy Foods
Frequent consumption of fast food can dull your taste buds and make healthier options less appealing. The intense flavors of fast foods, often enhanced by artificial additives, can overpower the subtler tastes of fruits and vegetables.
This can lead to a cycle where fast food becomes the preferred choice, further diminishing the desire for nutritious meals.
Reintroducing natural, flavorful foods into your diet can help reset your palate.


Increased Risk of Stroke
High sodium and trans fats in fast foods contribute to high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of stroke. Regularly consuming these foods can also lead to obesity, another major stroke risk factor.
Over time, these combined effects strain the cardiovascular system, making strokes more likely. Reducing fast food intake and adopting a heart-healthy diet can significantly lower this risk.


Impaired Kidney Function
Excessive sodium intake from fast foods can strain the kidneys, potentially leading to long-term damage. The kidneys work to filter out excess sodium, but chronic high-sodium diets can overwhelm their capacity, contributing to kidney disease.
Additionally, high blood pressure caused by fast food consumption is a leading cause of kidney damage. Staying hydrated and choosing low-sodium foods can help protect kidney health.

Please SHARE this with your friends and family.







